Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths on the uterus. They are fairly common amongst women of childbearing age—about 30% of women above the age of 35 will have uterine fibroids.
Uterine fibroids, also called myomas or leiomyomas, are composed of muscle and fibrous tissue. They come in different sizes, ranging from the size of a seedling to a bulky mass. Large fibroids can cause the abdomen to distend. When this happens, the fibroids can press on organs, resulting in increased pelvic pressure, frequent urge to urinate and difficulty passing motion. They can also cause heavy prolong menstrual bleeding. Fibroids can also contribute to infertility along with pregnancy and childbirth complications.
However, the risk of the fibroid being cancerous remains low and for the majority of women, it does not cause any symptoms nor affect daily activities.
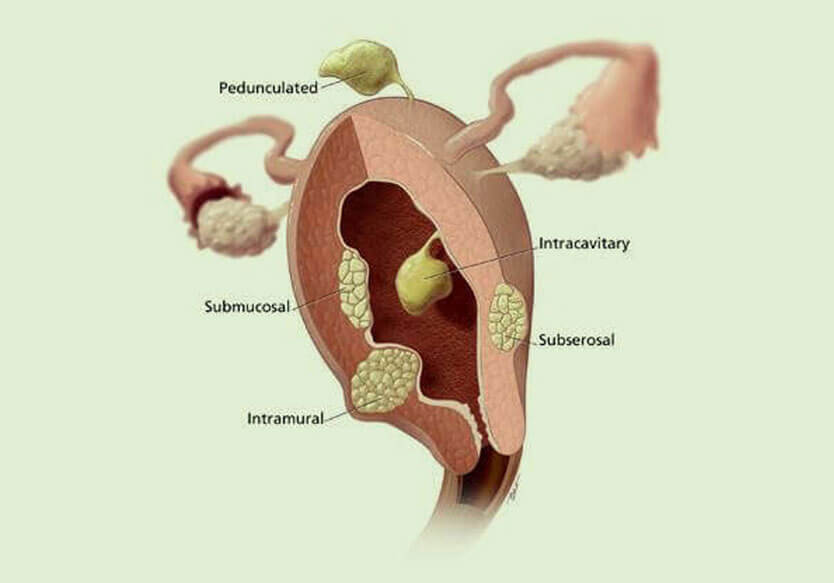
As uterine fibroids vary in size and numbers, women who display signs and symptoms often experience the following problems:
Although the exact cause of uterine fibroids is not fully understood, the following have been found to be possible factors contributing to the development of fibroids:
If you experience any of the above symptoms, we advise you to seek treatment. Options at our gynaecology clinic include observation, medication or surgery.
This is a surgical procedure to remove the fibroids while leaving the uterus intact. With myomectomy, there is a chance of the fibroids recurring in the future.
Patients who undergo this type of fibroid surgery experience decreased heavy menstrual bleeding and relief of pelvic pressure. This treatment is suitable for women who have fibroid symptoms and desire to have children in the future (fertility preservation).
A hysterectomy is the permanent solution to resolving fibroid problems. It involves removing the entire uterus which means that the patient will not be able to conceive in the future. The uterus, or womb, is where the foetus grows and develops. The uterus sheds its lining monthly in the form of menstruation so after a hysterectomy, a woman will also no longer have her monthly periods.
A hysterectomy is a recommendation made only when other treatments have failed to resolve the symptoms of uterine fibroids. Additionally, during fibroid surgery surrounding tissues and organs like the ovaries and fallopian tubes may also be removed.
Fibroids are common and benign growths on the uterus and they affect approximately 30% of women aged 35 and above.
Small fibroids that are asymptomatic may not require treatment. However, they may grow in response to oestrogen production. Some fibroids may also shrink in size after menopause, when oestrogen levels decrease.
Women who are 20–50 years old or premenopausal are usually at higher risk of developing fibroids. There are also other risk factors such as race, family history and obesity.
Fibroids can cause infertility because they can distort the shape of the cervical canal, which can impede the entry of sperm into the uterus. They can also alter the shape of the uterine cavity which impairs implantation of the embryo and lead to miscarriage or infertility.
Fibroids are usually not cancerous and only 1% will ever develop cancer. These tend to grow rapidly in size.
Do you have questions about women’s
health and pregnancy?
Let us help you.